Absolute Value
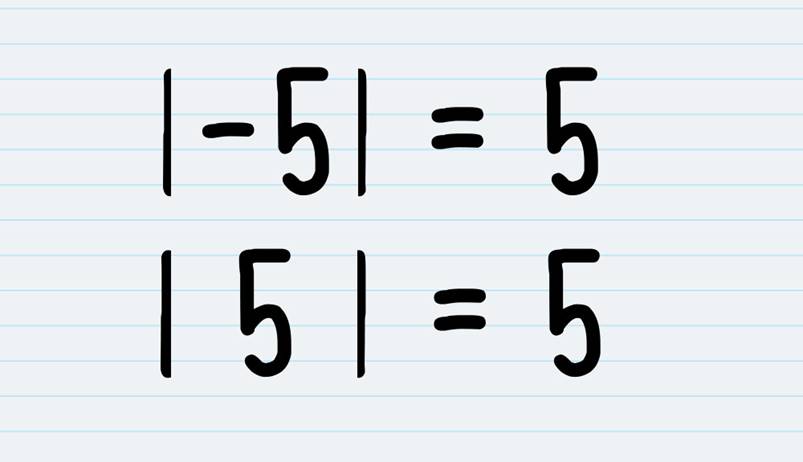
Overview
The absolute value of an
integer is the distance the integer is from zero on the number line.
The absolute value symbol is a
pair of vertical bars (I I).
Absolute value is always a
positive number.
It is the distance the number
is from zero on the number line.
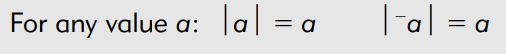
Letís
Practice
Complete the learning activity
below.
Absolute
Value of a Negative Integer
In mathematics, we often encounter negative numbers, which are less than
zero. Negative numbers can sometimes be confusing, especially when determining
their distance from zero. That's where the concept of absolute value comes into
play. Absolute value helps us find the distance of a number from zero,
regardless of whether it is positive or negative.
Let's focus on negative integers and explore how we can find their
absolute values. An integer is a whole number that can be positive, negative,
or zero. When talking about negative integers, we refer to numbers like -1, -2,
-3, and so on.
The absolute value of a negative integer is always a positive number. To understand
this, let's consider an example. If we have the number -3, its absolute value
would be 3. The absolute value symbol is denoted by vertical bars (| |). So, we
write the absolute value of -3 as |-3| = 3.
Here's a rule to remember: when you have a negative integer inside the
absolute value symbol, you drop the negative sign and write the number as a
positive value.
To find the absolute value of a negative integer, you can follow these
steps:
1. Identify the negative
integer you want to find the absolute value.
2. Remove the negative
sign. Imagine it's not there anymore.
3. Write the number as a
positive value.
Look at the example below.
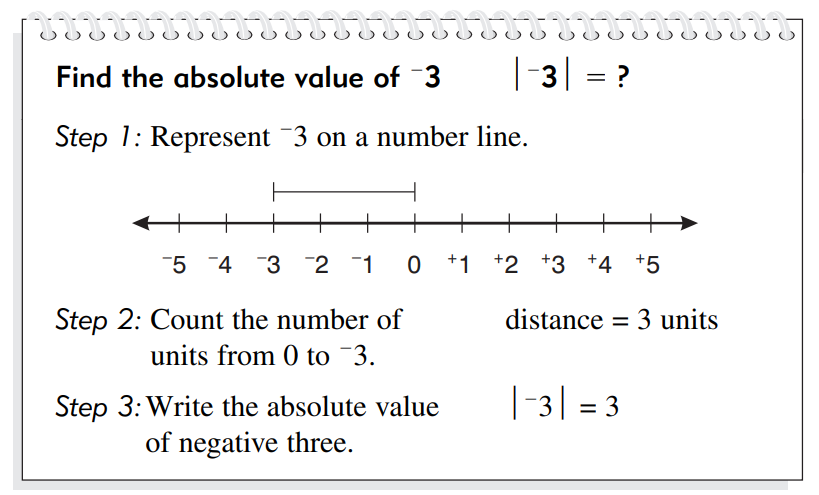
The absolute value of any negative integer is always equal to the
numerical value of the number without the sign.
Complete
the learning activity below.
username:
vla†† password:† student
Math Games: Absolute Value and Opposing Integers
Absolute
Value of a Positive Integer
In mathematics, we often work with positive numbers, which are numbers
greater than zero. When we want to find the distance of a positive number from
zero, we use the concept of absolute value. Absolute value helps us determine
the magnitude or size of a number, regardless of its sign.
Let's focus on positive integers and understand how to find their
absolute values. Positive integers are whole numbers like 1, 2, 3, etc.
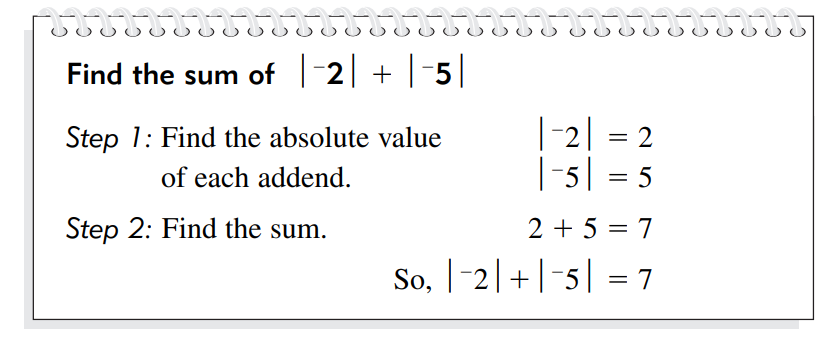
The absolute value of a positive integer remains the same. In other
words, if we have a positive number, its absolute value will also be positive.
For example, if we consider the number 4, its absolute value would be 4. We
write the absolute value of 4 as |4| = 4.
You don't need to change the number to find the absolute value of a
positive integer since it is already positive. The absolute value of a positive
integer is the number itself.
Remember that vertical bars (| |) denote the absolute value symbol. So,
when you see the absolute value symbol, you know that the result will be a
positive number.
Look at the example below.
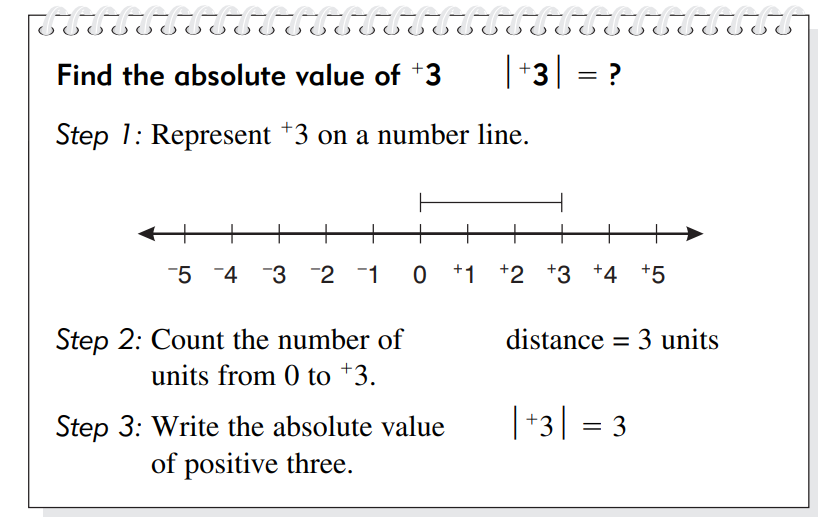
The absolute value of positive three represents 3 units above zero. The
absolute value of any positive integer is always equal to the numerical value
of the number without the sign.
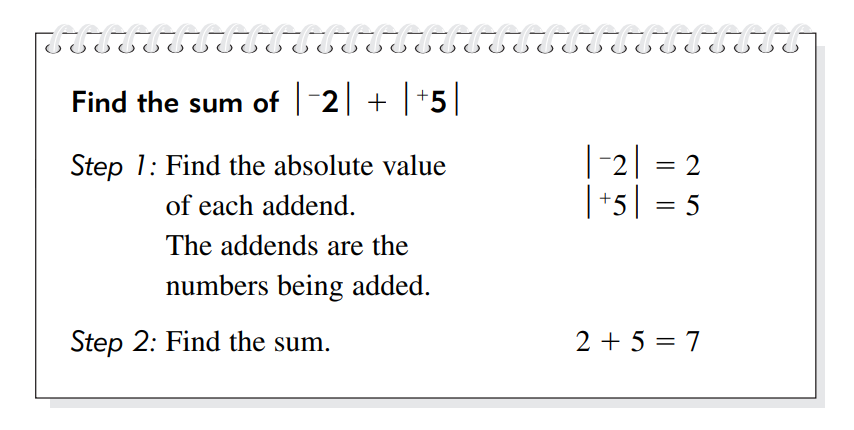
The absolute value of any positive or negative integer is the number
written without the positive or negative sign.
Let's Practice
Complete
the learning activity below.
username:
vla†† password:† student
Math Games: Absolute Value of Rational Numbers